Explain What the Different Ekg Waveforms Represent
In a normal ECG theres three distinct waves. Represents atrial depolarization which causes contraction as the electrical impulse spreads from the SA node through the atria usually 008 to 010 second.
The Example Of Ecg Five Waves Are Existed In Ecg They Are Called P Download Scientific Diagram
Large squares on the paper represents 02 seconds.

. The QRS complex represents depolarisation of the ventricles. Each ECG cycles consists of 5 waves. Its the first positive waveform following P wave.
The P wave the QRS complex and the T wave. Atrial depolarization spreads from the SA node towards the AV node and from the right atrium to the left atrium. Represents early ventricular depolarization.
The Q and S waves are below the base line and are known as negative waves. Not more that 5 mm in amplitude in standard leads and 10 mm in precordial leads. On the printed ECG each small square represents 004 sec.
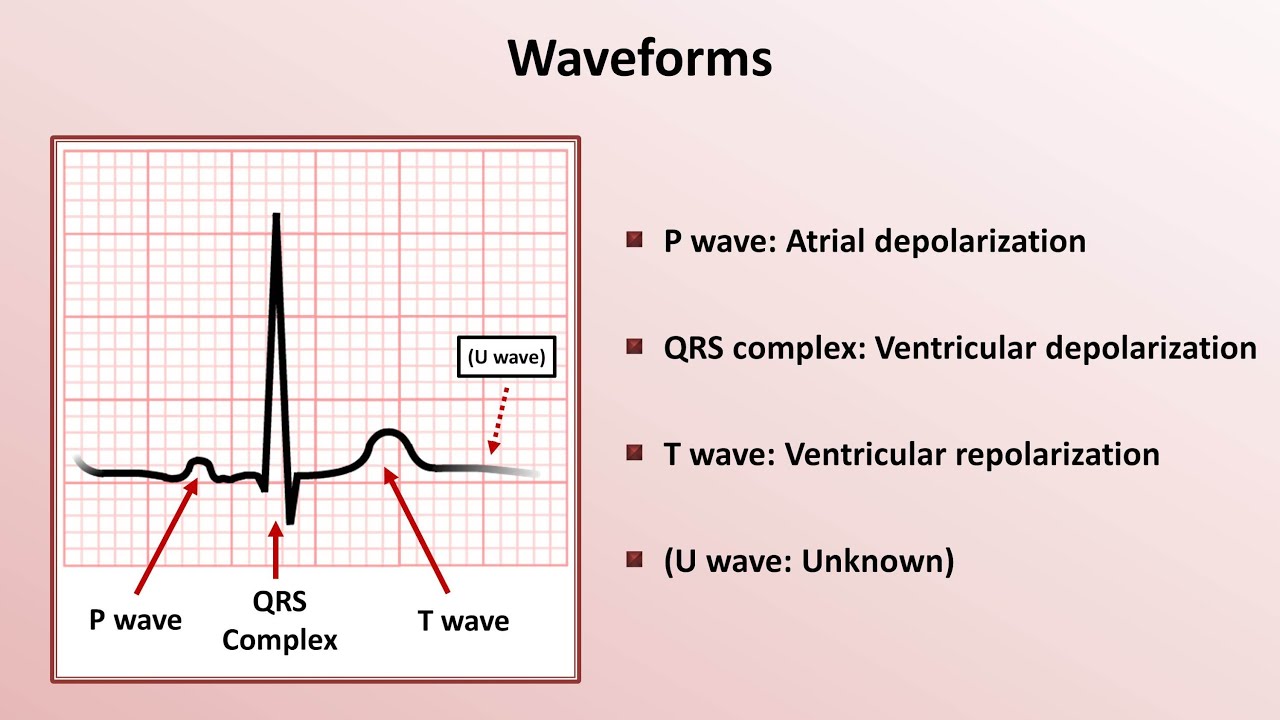
The first little hump or bump you see is known as the P-wave. Remember from the electrical conduction lecture that the SA node is responsible for this. 1 small box and 13 the height of the R wave in that lead.
It is a small smooth-contoured wave and represents atrial depolarisation. The Q and S-waves are below the base line and are known as negative waves. Normally not depressed more than 05 mm.
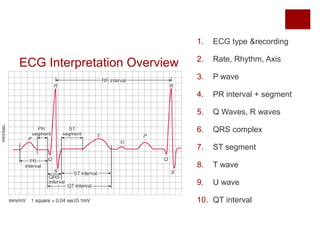
In summary whether the ECG is normal or abnormal it records just two basic events. Between the waveforms are the following segments and intervals. The T wave represents the re-polarization or recovery of the.
Which wave represent Atrial depolarization. It is measured from the beginning of the P wave until the beginning of the Q or R wave. Conversely a wave traveling away from the positive lead will inscribe a downward deflection.
P-waves represent atrial depolarization. In cases such as pre-excitation syndromes the PR interval may be shortened it. Duration of Q wave in the limb leads is 004 sec.
A typical human electrocardiogram has five waves P Q R S and T. As the ECG trace is recorded there are a series of upwards and downwards deflections created that represents atrial and ventricular depolarisation and repolarisation. ECG interpretation traditionally starts with an assessment of the P-wave.
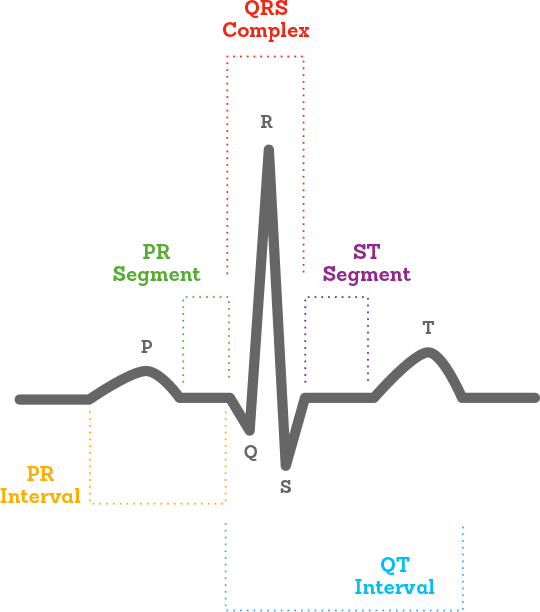
These are known as the ECG waves. The region between the QRS complex and T wave is referred to as the ST segment. The P-wave represents ATRIAL DEPOLARIZATION depolarization is a big fancy word for CONTRACTION.
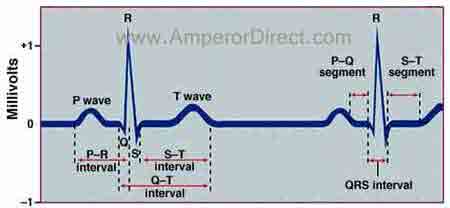
The PR interval begins at the start of the P wave and ends at the beginning of the Q wave. The P wave is of atrial origin while the Q R S and T waves are of. The P wave QRS complex and T wave are the parts of an EKG in which there are changes in voltage waves.
Duration of QRS complex is 006 to 010. The different waves that comprise the ECG represent the sequence of depolarization and repolarization of the atria and ventricles. Start studying EKG waves segments intervals and complex.
The first wave is the P wave which represents the depolarization of the atria. Is the electrical difference between the inside and outside of the cell. P QRS ST-T and U Waves.
The P wave represents the normal atrium upper heart chambers depolarization. The PR interval is assessed in order to determine whether impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricles. Leads and their geometry.
The P R and T-waves are above the base line and are known as positive waves. The QRS complex represents the depolarisation of the ventricles which leads to the ventricular contraction. The ECG is recorded at a speed of 25 mmsec 5 large squaressec and the voltages are calibrated so that 1 mV 10 mm 2 large squares in the vertical direction.
The QRS complex one single heart beat corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles lower heart chambers. P Q R S T corresponding to different phases of the heart activities. The PR interval represents the atrial depolarization and physiological delay of the stimulus in the atrioventricular AV node.
A wave that is travelling towards the positive lead will inscribe an upwards deflection of the EKG. It appears as three closely related waves on the ECG the Q R and S wave. They are the product of the action potentials created during the cardiac stimulation and repeated from one heart beat to another barring alterations.
Represents late ventricular depolarization. Heart diseases and irregular heartbeats can be detected in ECGs. The hearts electrical activity is represented on the monitor or ECG tracing by three basic waveforms.
The region between the P wave and QRS complex is known as the PR segment. There are mainly three types of ECG peak. Indicates early ventricular repolarization.
The P-wave PR interval and PR segment. The P-wave is of atrial origin while the Q R S and T-waves are of ventricular origin. Then the T wave shows that the electrical impulse has stopped spreading and the ventricles relax once again.
The P-wave reflects atrial depolarization activation. The EKG waveform comes from a measurement of surface voltages between 2 leads. The P-wave represents the depolarisation of the atria which leads to the contraction of both the atria.
The electrical impulse then reaches the ventricles. Learn the different waves of ECG P wave QRS complex R wave progression and more watch behind the scenes outtakes. This can be seen in the Q R and S waves of the ECG which is called the QRS complex.
The PR interval the PR segment the ST segment and the QT interval. What is the normal range for PR interval. Its normal value is between 012 s and 020 s.
The PR interval is the distance between the onset of the P-wave to the onset of the QRS complex. R waves are deflected positively and the Q and S waves are negative. A typical human electrocardiogram has five waves P Q R S and T.
Its the first negative waveform following the R wave. The region between 2 waves is called a segment. A brief period follows the P wave and represents the time in which the impulse is traveling within the AV node where.
The diagrammatic representation of a standard ECG is shown below. The P wave is the first positive deflection on the ECG. Waves are the different upward or downward deflections represented on the EKG tracing.
It represents the time taken for electrical activity to move between the atria and the ventricles. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The next area you see is a big spike.
A U wave is sometimes present. 1 depolarization the spread of a stimulus through the heart muscle and 2 repolarization the return of the stimulated heart muscle to the resting state. The P R and T waves are above the base line and are known as positive waves.
Ecg Interpretation Characteristics Of The Normal Ecg P Wave Qrs Complex St Segment T Wave Ecg Echo
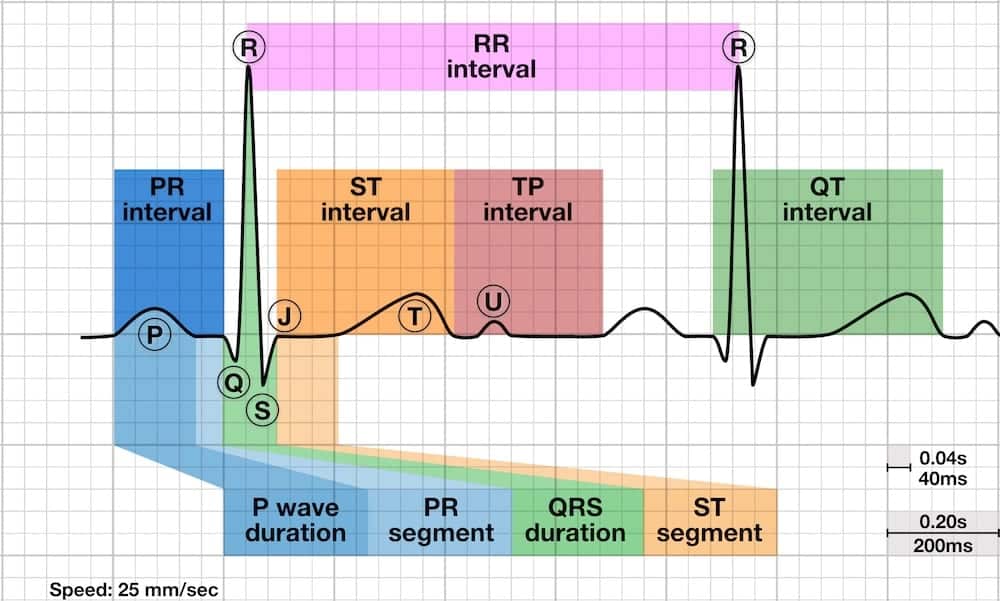
Pr Interval Litfl Ecg Library Basics

Electrocardiograms Cardiac Nursing Icu Nursing Nursing School Tips

The Cardiac Cycle Cardiac Cycle Cardiac Muscle Cell Cardiac Nursing
Ecg Signal Waveform Forms Namely Time Domain And Frequency Domain Download Scientific Diagram
A Typical Ecg Waveform And Its Characteristic Patterns P And T Waves Download Scientific Diagram
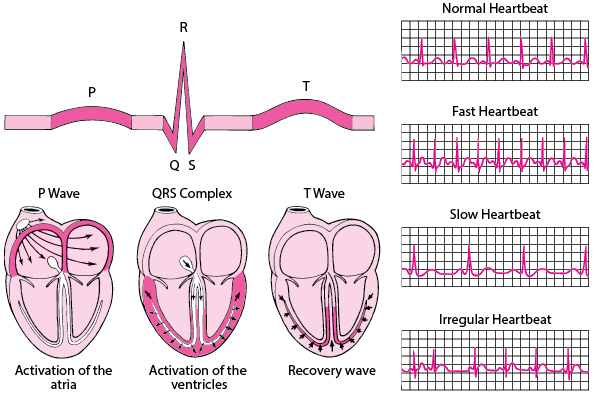
Electrocardiography Heart And Blood Vessel Disorders Msd Manual Consumer Version

Aidet Explained In Detail Caregiverology Nursing School Survival Nursing Mnemonics Medical Mnemonics
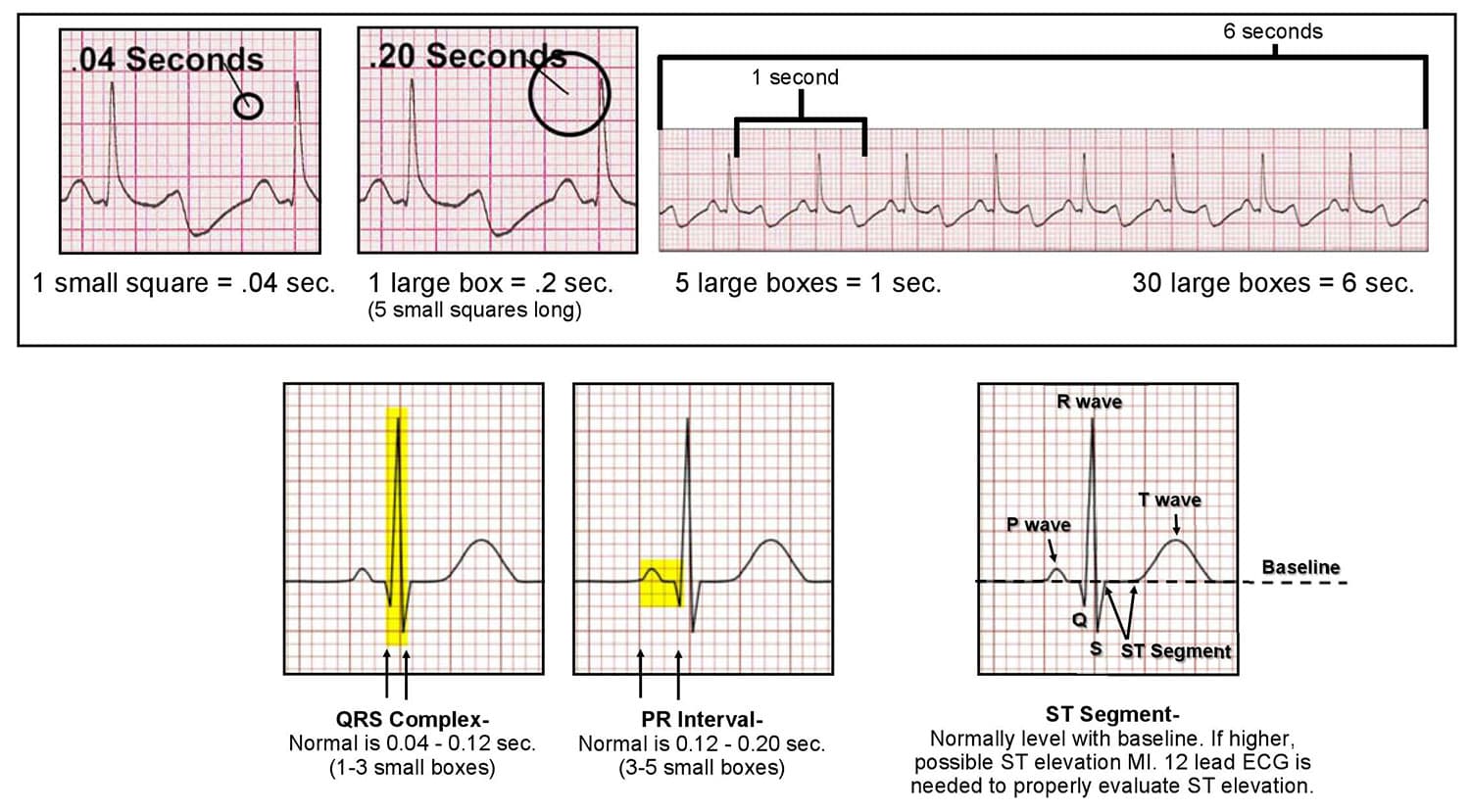
How To Read And Interpret An Ecg Ekg Acls Wiki
Intro To Ekg Interpretation Waveforms Segments And Intervals Youtube

Schematic Representation Of Ecg Waves Intervals And Segments For A Download Scientific Diagram

Vascular Ultrasound Renal Diagnostic Medical Sonography

Ecg Normal Waveforms Google Search Heart Blocks Pr Interval Qrs Complex

Pin On All About Nursing Things To Help Me Remember Because My Brain Is So Full That It May Explode

Pin By Max Moua On Nursing School Study Tools Nursing School Problems Medical Nursing School Studying

Comments
Post a Comment